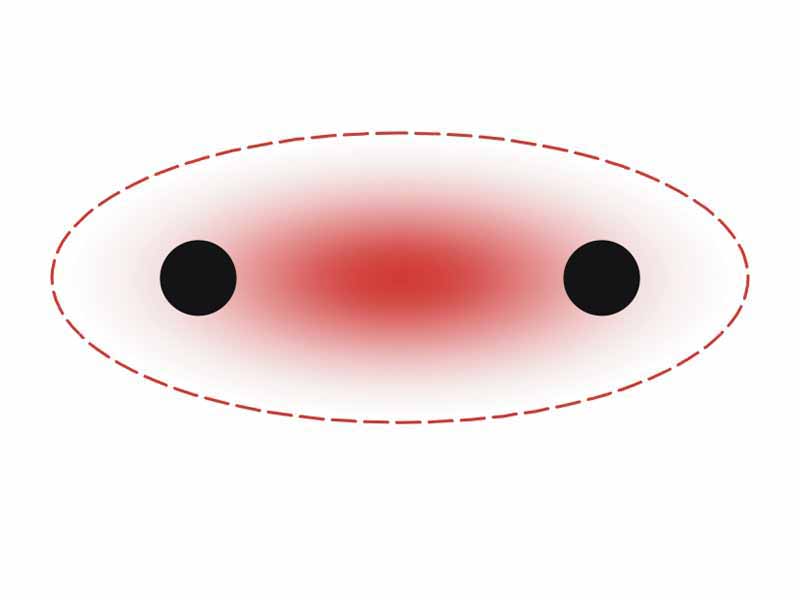
Within the context of our discussion of covalent bonding, let's reprise an important point regarding the underlying coherence of the oxidation-reduction method of describing chemical reactions. In covalent bond formation, internal energy decreases as electrons form molecular orbitals and draw the nuclei inward along the bond axis to form the bond between the atoms. Further energy is lost by the system when a polar bond forms as the bonded electrons are drawn in toward the more electronegative atom.
Polar bond formation represents an additional internal energy decrease. For this reason, polar bonds tend to be stronger than non polar bonds. This underlying concept is the basis for oxidation-reduction. The graphs of the electronegativities of the elements and their reduction potentials closely agree. Electronegative atoms pull electrons in closely when they form bonds, which is a favorable development from the point of view of energy.
This is the true inside story of redox. Oxidation-reduction gives a systematic way to account for this phenomenon by representing the chemical reaction process as a narrative of 'electron control' and standardizing the energy involved in tables of reduction potentials.