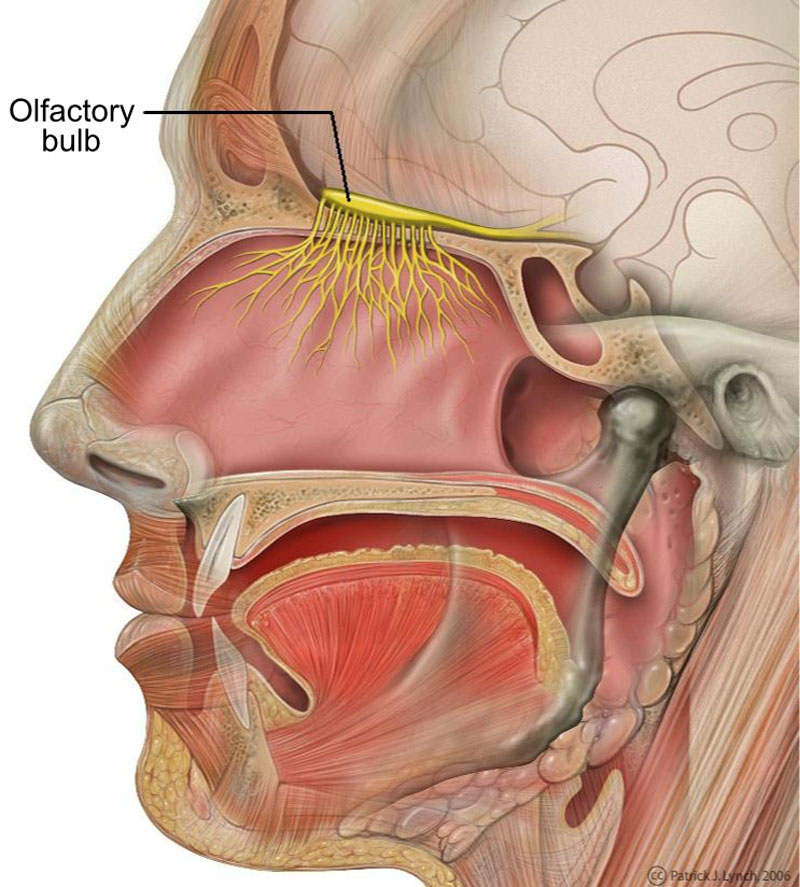
Smell
- Olfaction is the sense of smell.
- Olfactory neuron receptor molecules are responsible for the detection of odor molecules. Activation of these receptors is the initial player in a signal transduction cascade which ultimately produces a nerve impulse which is transmitted to the brain.
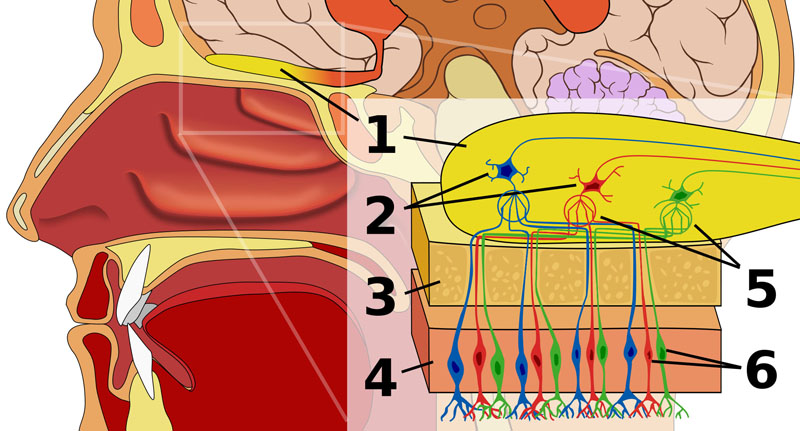
Human olfactory system. 1: Olfactory bulb 2: Mitral cells 3: Bone 4: Nasal epithelium 5: Glomerulus 6: Olfactory receptor neurons.
- Located on the inferior side of the brain, the olfactory bulb is the primary neural structure of the vertebrate forebrain involved in olfaction, or the sense of smell.
- The olfactory tract is a bundle of axons connecting the mitral and tufted cells of the olfactory bulb to several target regions in the brain.