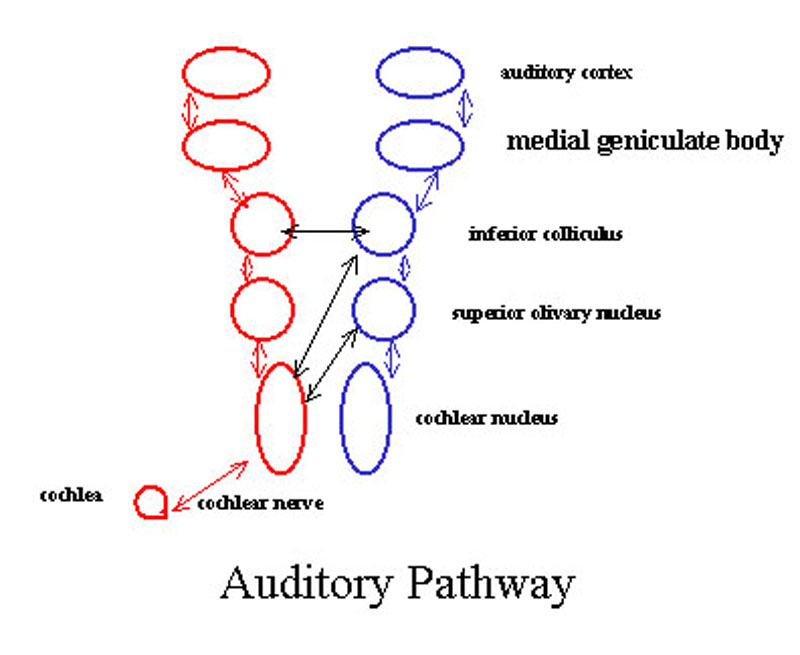
Auditory Pathways
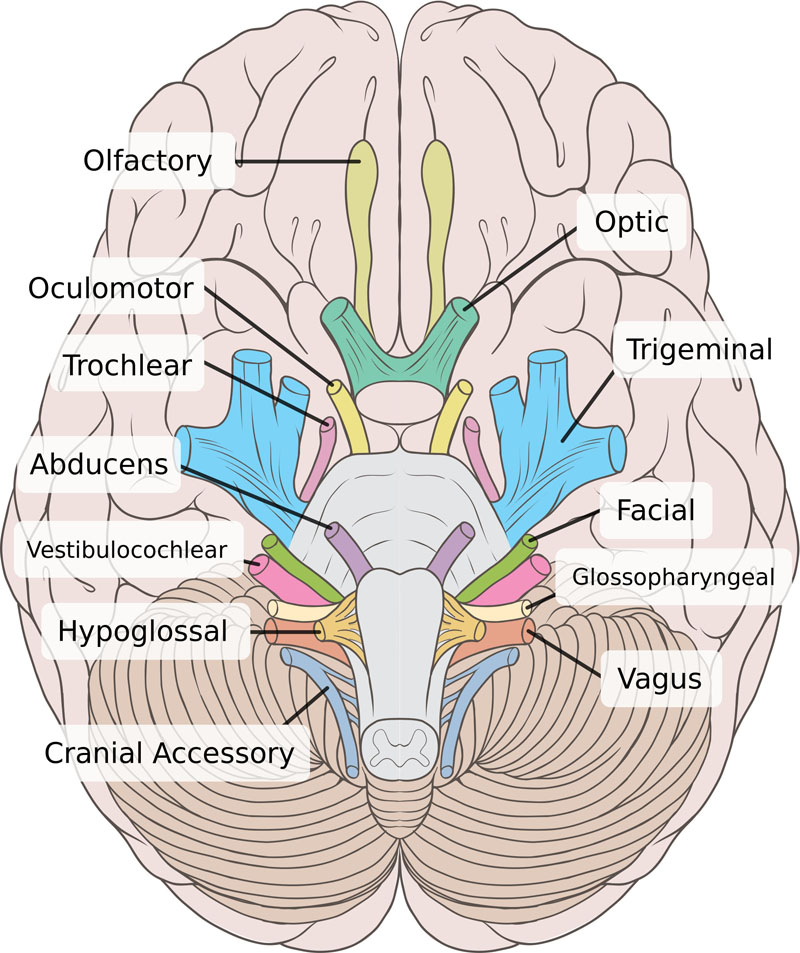
- The vestibulocochlear nerve, the eighth cranial nerve, transmits sound and equilibrium information from the inner ear to the brain.
- The superior olivary complex is a collection of brainstem nuclei that functions in multiple aspects of hearing and is an important component of the ascending and descending auditory pathways of the auditory system.
- The inferior colliculus is the principal midbrain nucleus of the auditory pathway and receives input from several peripheral brainstem nuclei in the auditory pathway, as well as inputs from the auditory cortex.
- The medial geniculate nucleus is part of the auditory thalamus and represents the thalamic relay between the inferior colliculus and the auditory cortex.
- The primary auditory cortex is the part of the temporal lobe that processes auditory information in humans and other vertebrates.