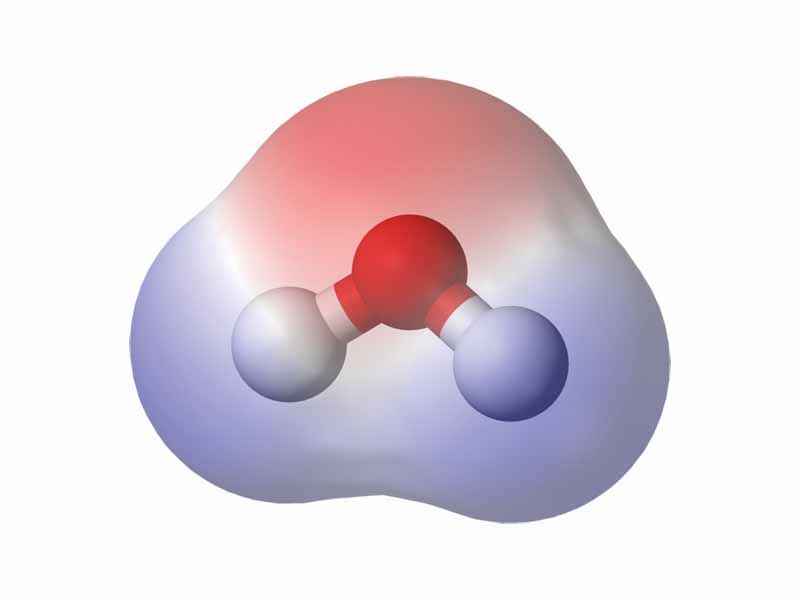
A commonly-used example of a polar compound is water (H2O). The electrons of water's hydrogen atoms are strongly attracted to the oxygen atom, and are actually closer to oxygen's nucleus than to the hydrogen nuclei; thus, water has a relatively strong negative charge in the middle (red shade), and a positive charge at the ends (blue shade).
Click this LINK to visit the original image and attribution information. Right click on the image to save the 800px teaching JPEG.