The Endocrine System
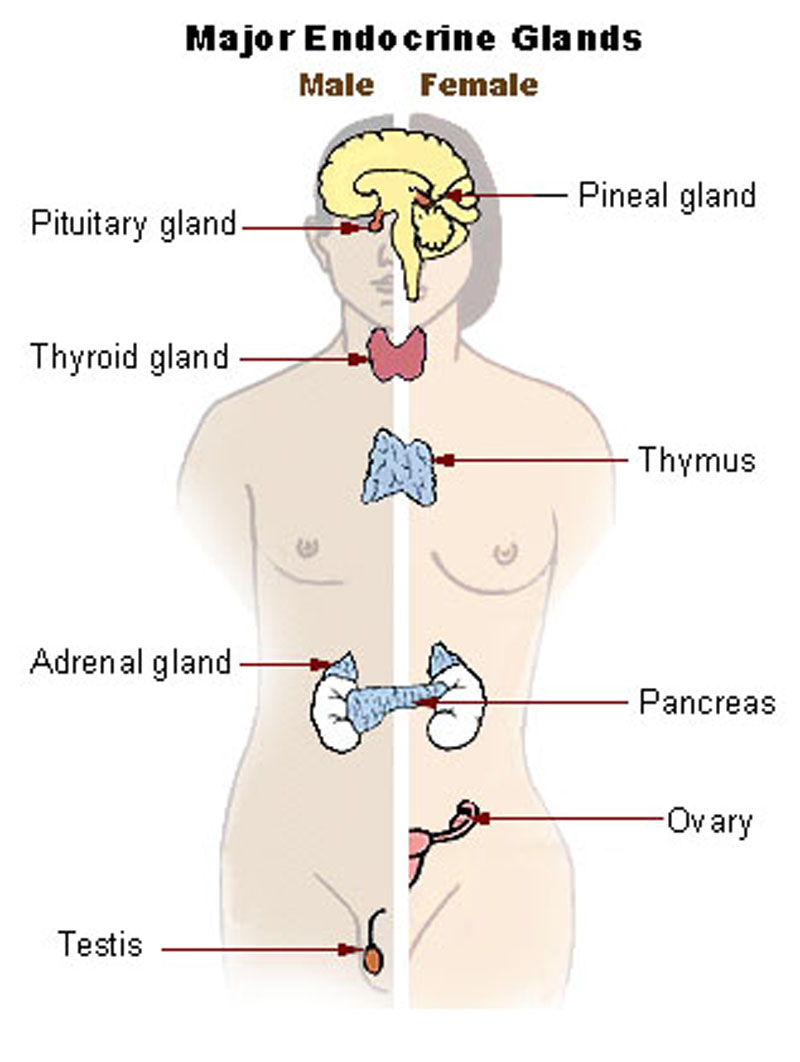
- The endocrine system refers to the collection of glands of an organism that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried towards distant target organs.
- A hormone is any member of a class of signaling molecules produced by glands in multicellular organisms that are transported by the circulatory system to target distant organs to regulate physiology and behaviour.
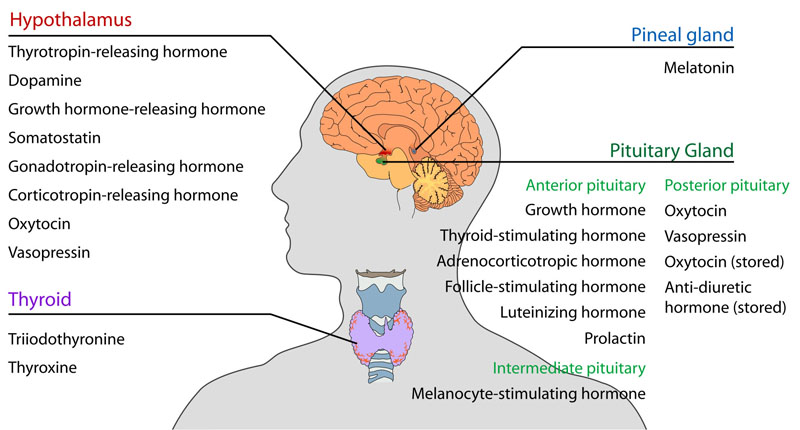
- The hypophyseal portal system is a system of blood vessels in the brain that connects the hypothalamus with the anterior pituitary.
- A protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus, the pituitary gland secretes hormones that help control: growth, blood pressure, sex organ functions, metabolism, some aspects of pregnancy, childbirth, nursing, water/salt concentration, temperature regulation and pain relief.
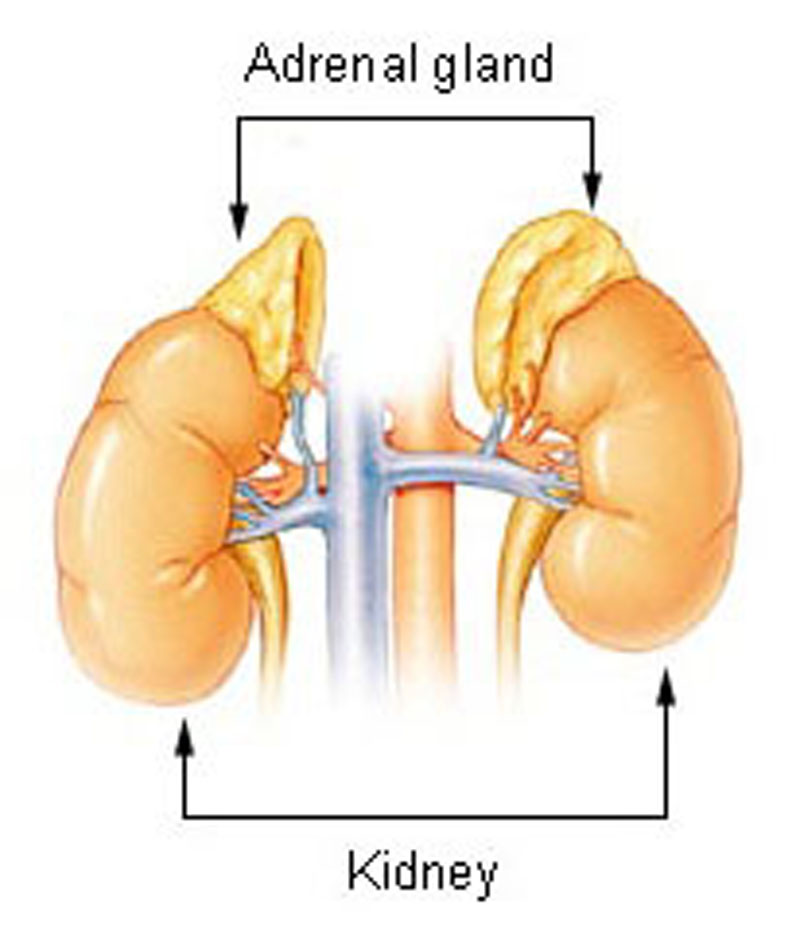
- The adrenal glands are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including epinephrine and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol.
- The adrenal medulla is the innermost part of the adrenal gland, consisting of cells that secrete epinephrine, norepinephrine, and a small amount of dopamine in response to stimulation by sympathetic preganglionic neurons.
- Situated along the perimeter of the adrenal gland, the adrenal cortex mediates the stress response through the production of mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids, such as aldosterone and cortisol, respectively. It is also a secondary site of androgen synthesis.
- Steroid hormones produced in the adrenal cortex, corticosteroids are involved in a wide range of physiological processes, including stress response, immune response, and regulation of inflammation, carbohydrate metabolism, protein catabolism, blood electrolyte levels, and behavior.
- Cortisol is a steroid hormone produced in the adrenal cortex released in response to stress and low blood-glucose concentration.
- Epinephrine is produced by both the adrenal glands and certain neurons. It plays an important role in the fight-or-flight response by increasing blood flow to muscles, output of the heart, pupil dilation, and blood sugar.
- The principle male sex hormone, testosterone is a steroid hormone secreted primarily by the testicles of males and, to a lesser extent, the ovaries of females. Small amounts are also secreted by the adrenal glands.
- Estrogen is the primary female sex hormone and is responsible for development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics.
- A gonad is an endocrine gland that produces the gametes (germ cells) of an organism.
- Libido, colloquially known as sex drive, is a person's overall sexual drive or desire for sexual activity. Sex drive is determined by biological, psychological and social factors.