Motor Development
- A reflex is an involuntary and nearly instantaneous movement in response to a stimulus.
- Primitive reflexes are reflex actions originating in the central nervous system that are exhibited by normal infants, but not neurologically intact adults, in response to particular stimuli.
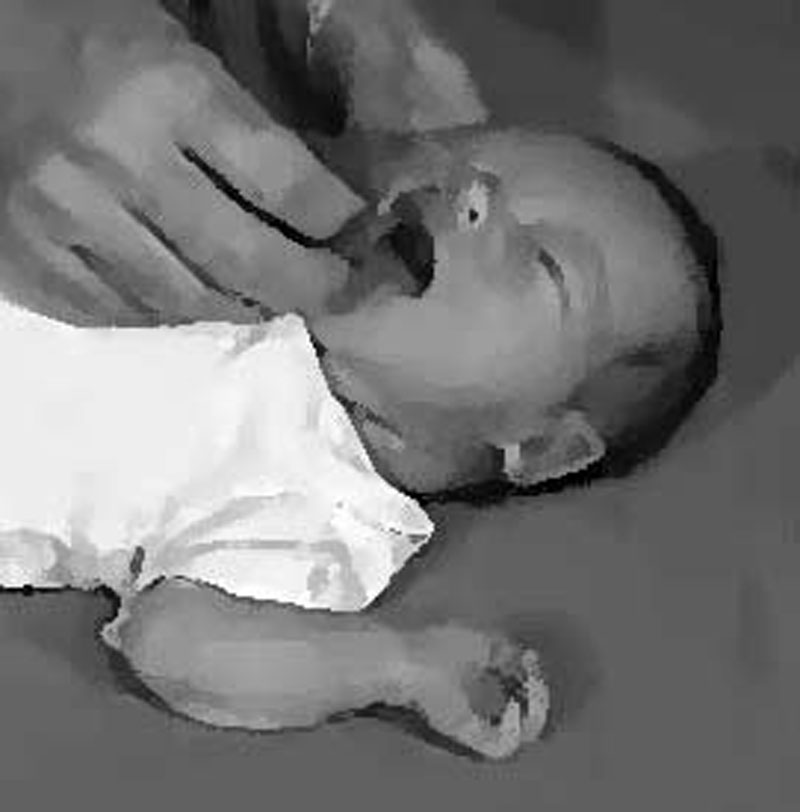
- A reflex action by which an infant turns its head toward anything that strokes its cheek or mouth, the rooting reflex is present at birth and disappears around four months of age.
- The Moro reflex is an infantile reflex normally present in all infants/newborns up to 4 or 5 months of age as a response to a sudden loss of support. It involves three distinct components: spreading out the arms, unspreading the arms, and crying.
- An upward response (extension) of the big toe when the sole of the foot is stimulated with a blunt instrument is known as the Babinski sign, which can identify disease of the spinal cord and brain in adults, and also exists as a primitive reflex in infants.
- Gross motor skills are the abilities usually acquired during infancy and early childhood as part of a child's motor development. By the time they reach two years of age, almost all children are able to stand up, walk and run, walk up stairs, etc.
- Fine motor skill (or dexterity) is the coordination of small muscle movements - usually involving the synchronization of hands and fingers - with the eyes.