Biological Approaches to Behavior
The Limbic System
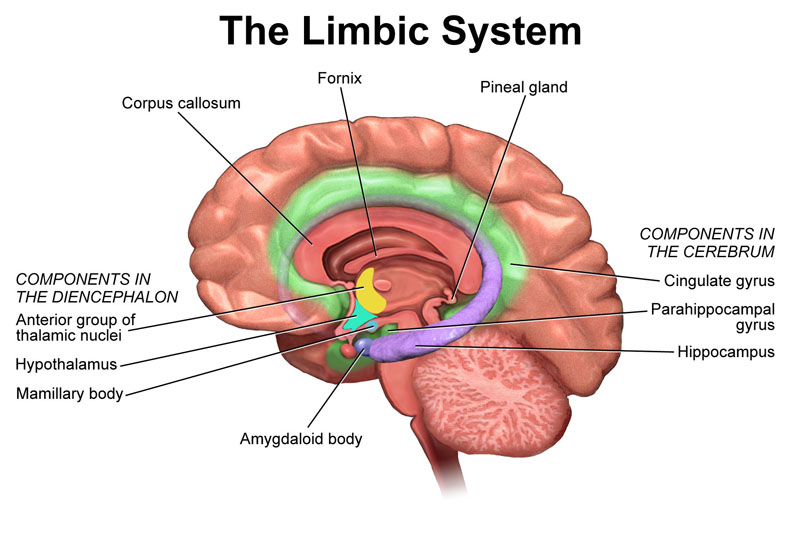
- The limbic system is a collection of structures on both sides of the thalamus that supports a variety of functions including epinephrine flow, emotion, behavior, motivation, long-term memory, and olfaction.
- Among other functions, the hypothalamus links the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland.
- In neuroanatomy, a nucleus is a cluster of densely packed cell bodies of neurons in the central nervous system, located deep within the cerebral hemispheres and brainstem.
- The amygdalae are two almond-shaped groups of nuclei located within the temporal lobes which perform a primary role in the processing of memory, decision-making, and emotional reactions.
- The cingulate cortex, also called the limbic cortex, is involved with emotion formation and processing, learning, and memory. It plays an important role in linking behavioral outcomes to motivation.
- The hippocampus belongs to the limbic system and plays important roles in the consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory and spatial navigation.