Stimulant Drugs: Tobacco, Cocaine, and Amphetamine
- Stimulants are psychoactive drugs that induce temporary improvements in either mental or physical functions or both.
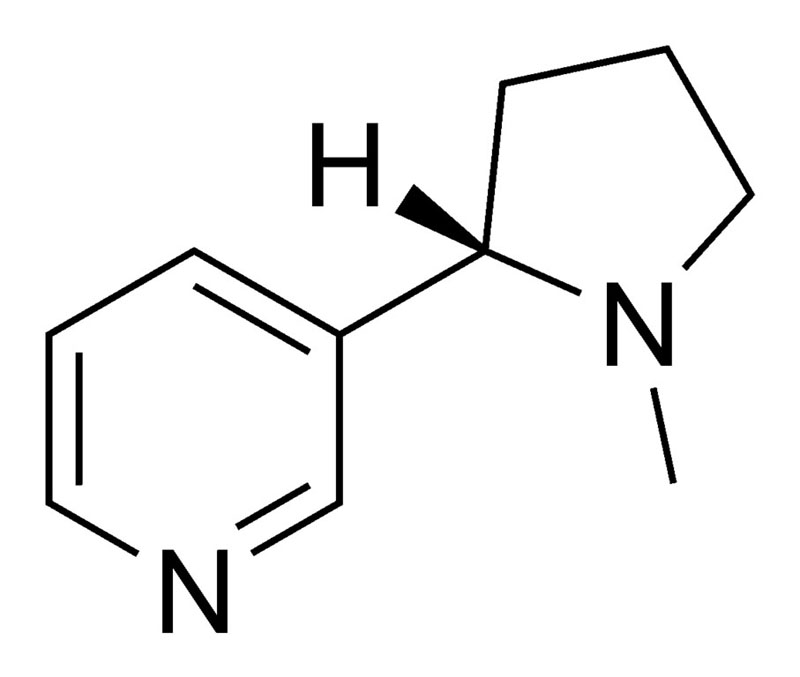
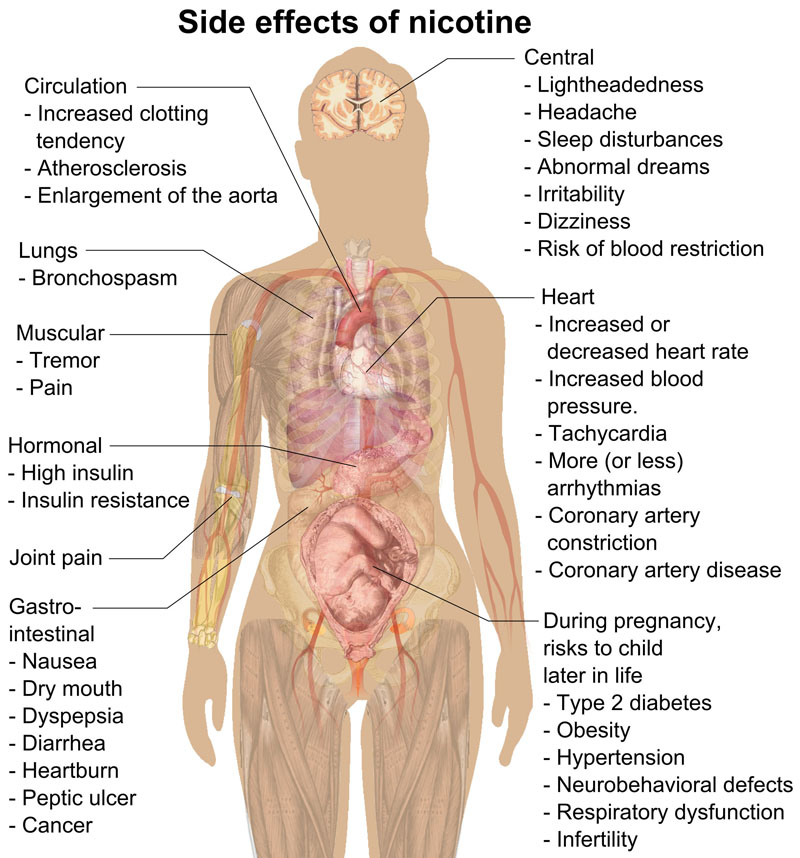
- The plant tobacco contains the alkaloid nicotine, a stimulant. The use of this plant, particularly in smoking, is a risk factor for many diseases, especially those affecting the heart, liver, and lungs, and several cancers.
- Nicotine is a potent parasympathomimetic alkaloid found in the nightshade family of plants and is a stimulant drug.
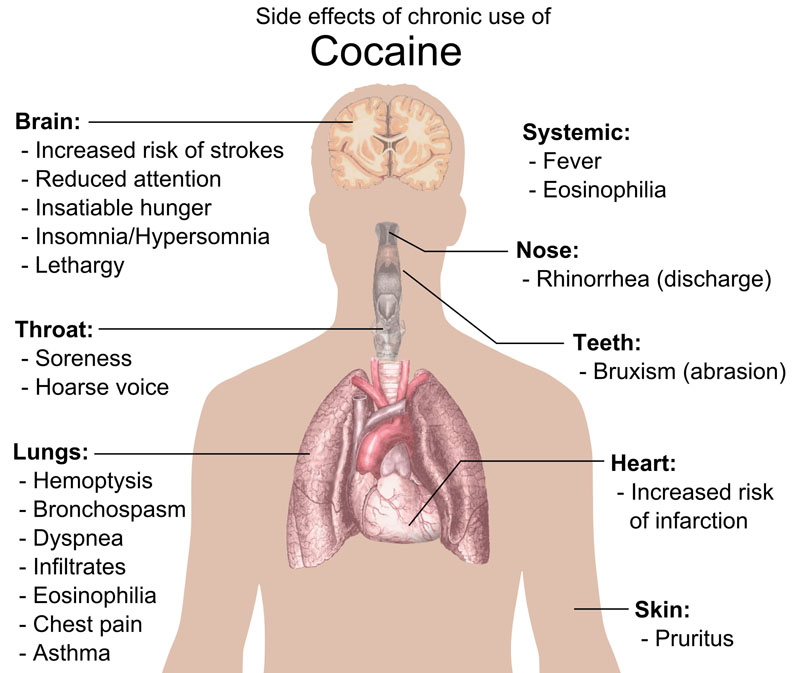
- Cocaine, also known as benzoylmethylecgonine, is a strong stimulant. It is commonly snorted, inhaled, or injected into the veins. Mental effects may include loss of contact with reality, an intense feeling of happiness, or agitation.
- The class of substituted methamphetamines span a variety of pharmacological subclasses, including stimulants, entactogens, hallucinogens, among others. Examples from this class of drugs include ephedrine, cathinone, MDMA (ecstasy), and DOM (STP).
- Methamphetamine is a strong central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is mainly used as a recreational drug. Chronic high dose use can precipitate unpredictable and rapid mood swings, prominent delusions and violent behavior.