Hallucinogens
- A hallucinogen is a psychoactive agent which can cause hallucinations, perception anomalies, and other substantial subjective changes in thoughts, emotion, and consciousness. Common types are psychedelics, dissociatives, or deliriants.
- A psychedelic substance is a psychoactive drug whose primary action is to alter cognition and perception, typically by agonising serotonin receptors.
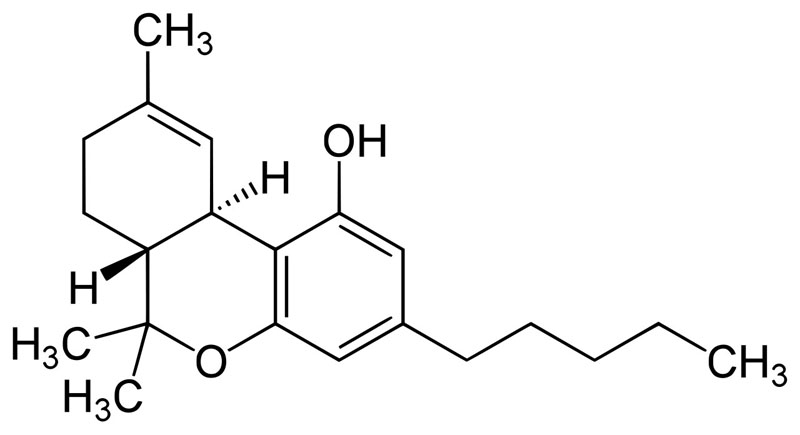
- Cannabis, also known as marijuana, is often consumed for its mental and physical effects, such as heightened mood, relaxation, and an increase in appetite.
- Tetrahydrocannabinol is the principal psychoactive constituent of cannabis.
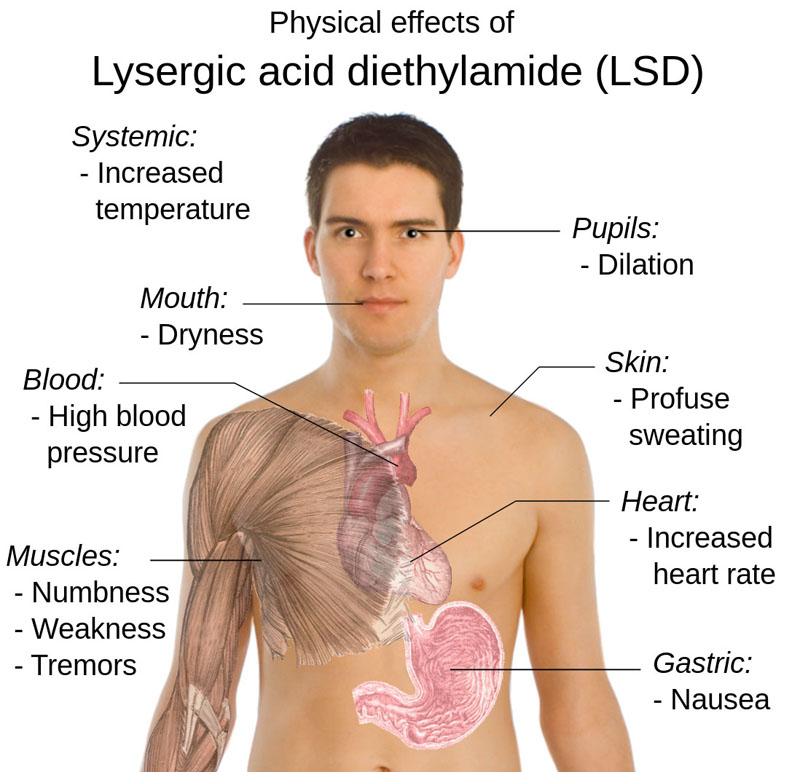
- LSD is a psychedelic drug of the ergoline family, well known for its psychological effects - which can include altered thinking processes, closed- and open-eye visuals, synesthesia, an altered sense of time, and spiritual experiences.
- Ecstasy (MDMA) is a psychoactive drug consumed primarily for its euphoric and empathogenic effects. Pharmacologically, it acts as a serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine releasing agent and reuptake inhibitor.