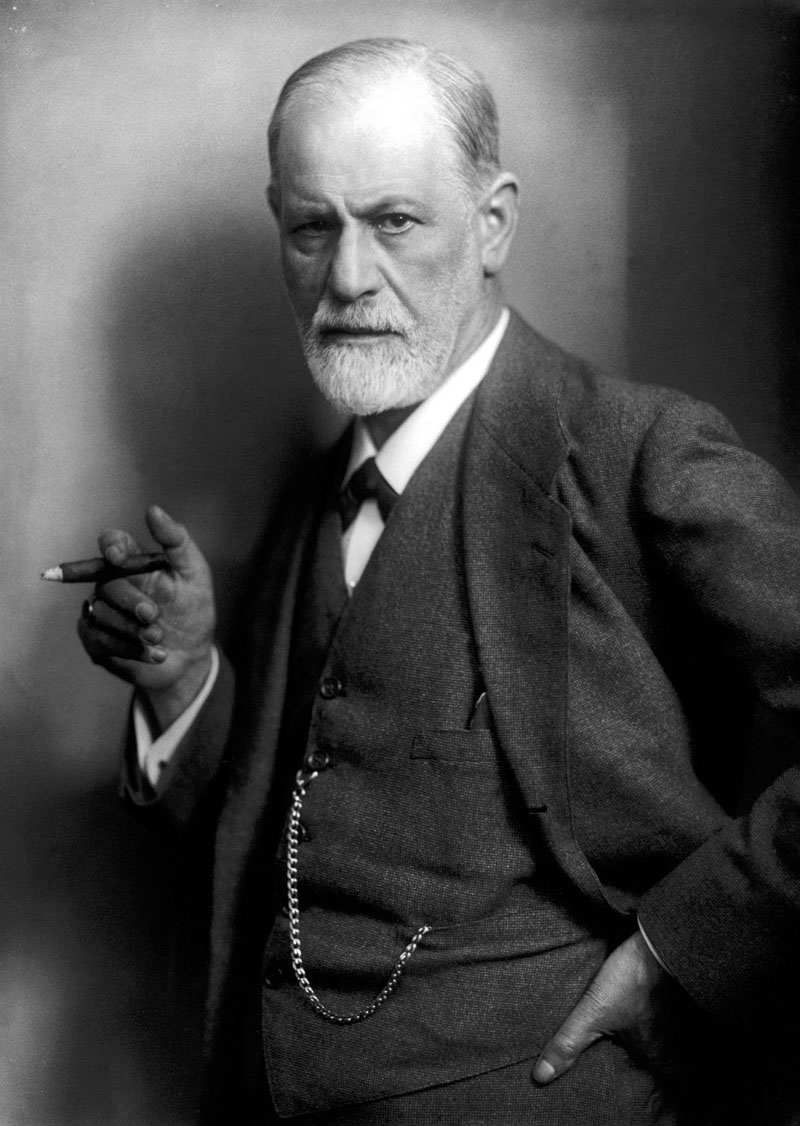Freud's Psychoanalytic Theory
- Sigmund Freud was an Austrian neurologist, now known as the father of psychoanalysis.
- The psyche is the totality of the human mind, conscious and unconscious.
- Psychic determinism theorizes that all mental processes are not spontaneous but are determined by the unconscious or preexisting mental complexes.
- A symbol is an object or a concept that represents, stands for or suggests another idea, visual image, belief, action or material entity.
- Psychodynamics emphasizes systematic study of the psychological forces that underlie human behavior, feelings, and emotions and how they might relate to early experience. It is especially interested in the dynamic relations between conscious motivation and unconscious motivation.
- The unconscious mind consists of the processes in the mind that occur automatically and are not available to introspection, and include thought processes, memory, affect, and motivation.
- In Freud's structural model of the psyche, the id is the unorganized part of the personality structure that contains a human's basic, instinctual drives. It is the only component of personality that is present from birth.
- In Freudian psychoanalysis, the pleasure principle is the instinctual seeking of pleasure and avoiding of pain in order to satisfy biological and psychological needs. Specifically, it is the driving force guiding the id.
- In Freud's structural model of the psyche, the ego seeks to please the id's drive in realistic ways that will benefit in the long term rather than bring grief.
- In Freudian psychology and psychoanalysis, the reality principle is the ability of the mind to assess the reality of the external world, and to act upon it accordingly, as opposed to acting on the pleasure principle.
- In Freud's structural model of the psyche, The superego reflects the internalization of cultural rules, mainly taught by parents applying their guidance and influence.

An iceberg is often used to provide a visual representation of Freud’s theory that most of the human mind operates unconsciously.