Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy works to solve current problems and change unhelpful thinking and behavior using a combination of basic behavioral and cognitive principles. It was originally designed to treat depression, but is now used for a number of mental disorders.
- A cognitive distortion is an exaggerated or irrational thought patterns that is believed to perpetuate the effects of psychopathological states, especially depression and anxiety.
- Dialectical behavior therapy is designed to help people change patterns of behavior that are not helpful, such as self-harm and substance abuse. It works towards helping people learn about the triggers that lead to reactive states and which coping skills to apply to help avoid undesired reactions.
- Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy is a long-standing form of cognitive-behavior therapy. A fundamental premise is that humans do not get emotionally disturbed by unfortunate circumstances, but by how they construct their views of these circumstances.
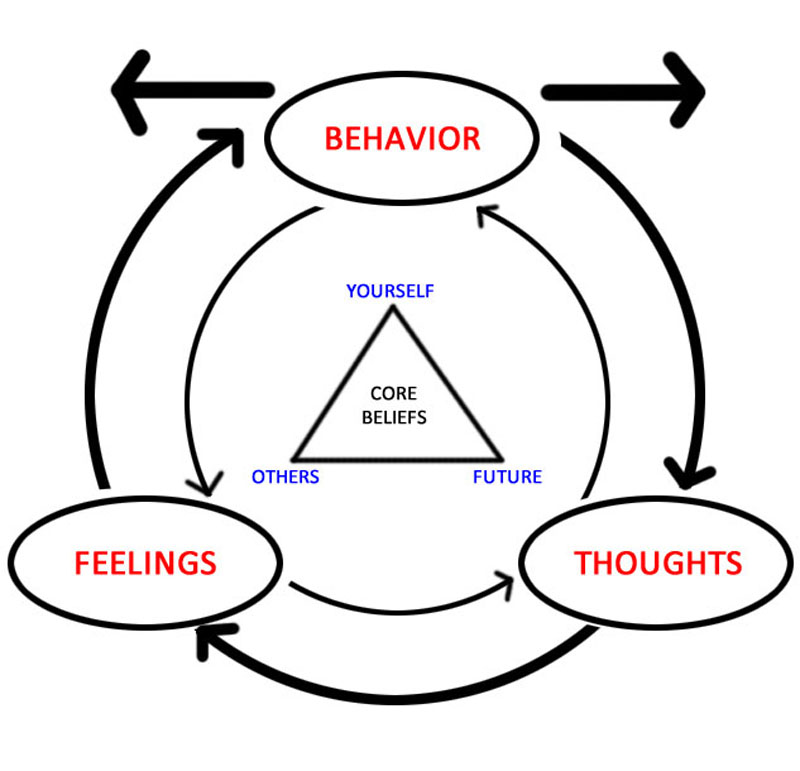
The diagram depicts how emotions, thoughts, and behaviors all influence each other. The triangle in the middle represents cognitive behavior therapy's tenet that all humans' core beliefs can be summed up in three categories: self, others, future.