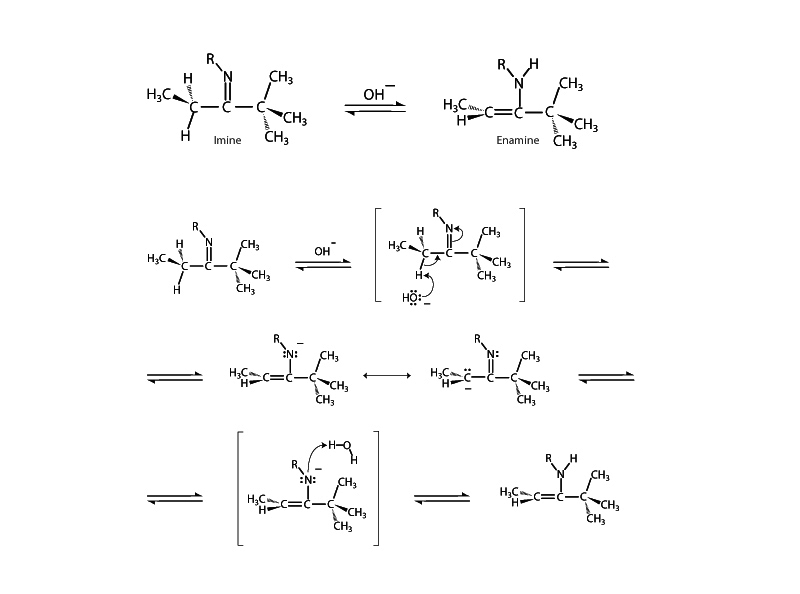
In aqueous solution an equilibrium will be established between an imine (or Schiff base) and its enamine tautomer, if the imine possesses an α hydrogen, in much the same way that we see an equilibrium established between and aldehyde or ketone and its enol tautomer. Imine-enamine tautomerism is the nitrogen analog to keto-enol tautomerism. In both cases, a hydrogen atom exchanges between the heteroatom (oxygen or nitrogen) and the second carbon atom.
An enamine tautomer behaves a lot like an enol, and like enols, enamines are nucleophilic at the α carbon. When you see an imine in solution, you should also recognize that the enamine tautomer will also be present in some percentage. Imine-enamine tautomerism gives imines a whole set of possible reaction pathways arising from the nucleophilicity of the α carbon.