Interdisciplinary Note (5 of 11)
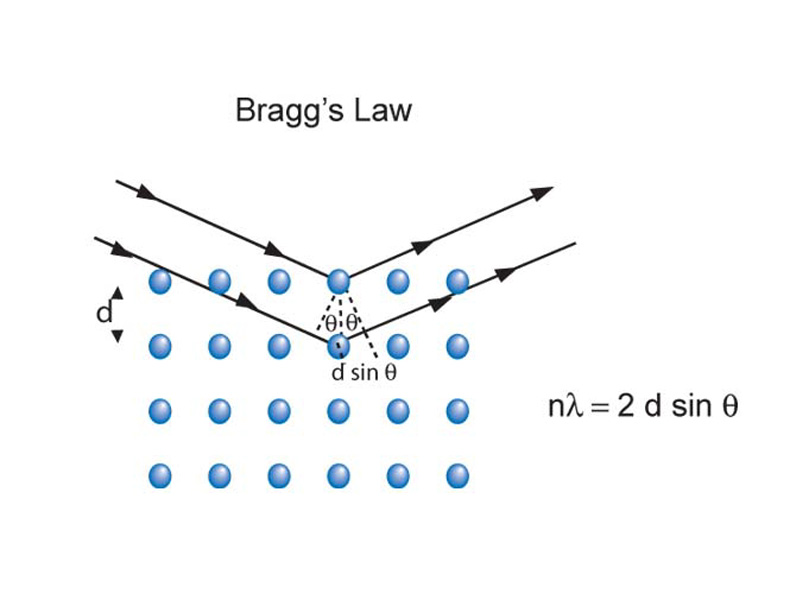
In x-ray crystallography, the array of atoms in a crystal acts like a three-dimensional diffraction grating. The spacing in a solid is on the order of 10-10 m, which is on the order of the wavelength of x-rays. In other words, because x-ray wavelengths are at the angstrom level, x-rays make ideal measuring tools for the structure of substances.
In x-ray crystallography, constructive interference can be predicted by Bragg's law, allowing crystal layer spacing to be infered from the angles at which x-rays at a given wavelength bounding off different layers of the crystal experience constructive interference.