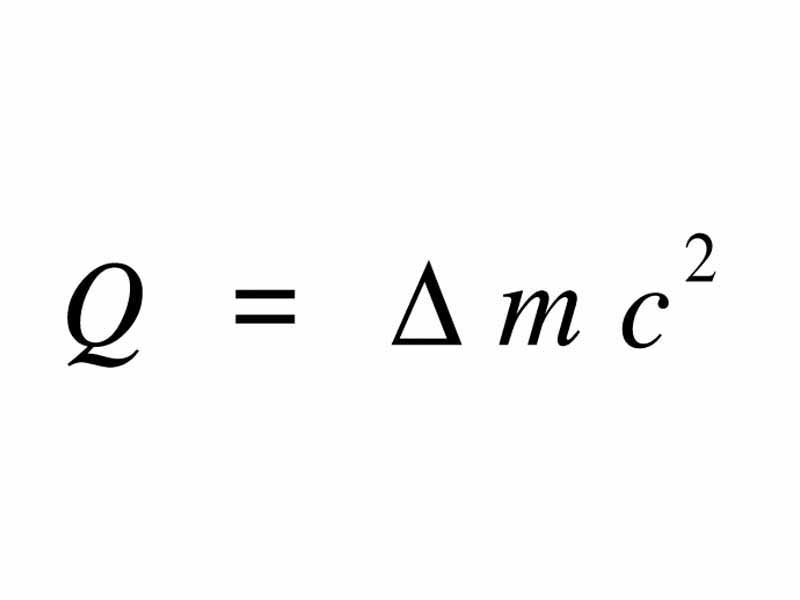Interdisciplinary Note (6 of 11)
In nuclear physics, internal energy change maps onto change in rest mass. For a possible nucleus to have any binding energy whatsoever, nuclear mass must be less than the sum of the masses of the individual nucleons. This means that because of mass-energy equivalence, the internal energy of the nucleus is less than the energy of the separated nucleons.