Interdisciplinary Note (10 of 20)
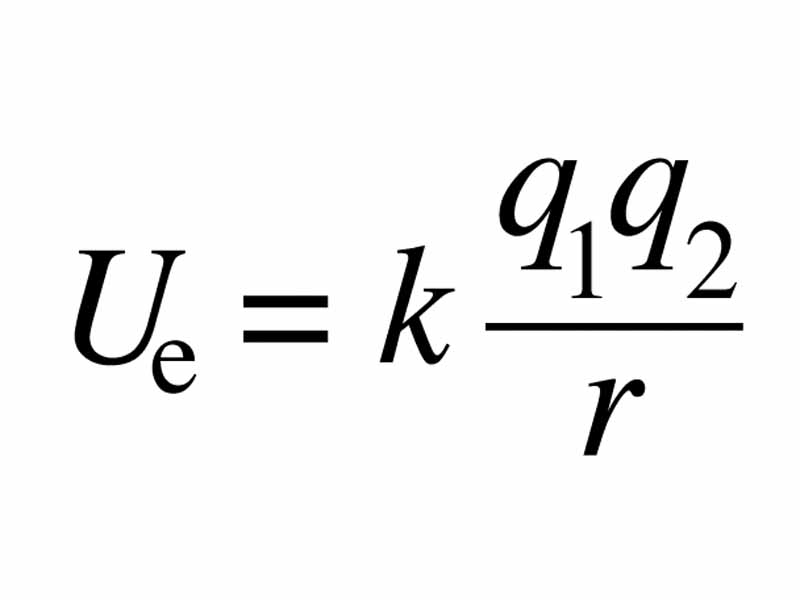
When a positive charge is moved towards another positive charge, potential energy increases. Energy is being stored in the system. However, when a negative charge is moved towards a positive charge, potential energy decreases and the system is losing potential energy.
The behavior of oppositely charged particles, distinguished by a force of mutual attraction, is similar to gravitational force. The energy description of oppositely charged particles is analogous to the behavior of two masses interacting through gravitational force. The nearer the objects, the lower the potential energy with both gravitational force between masses and the electric force between unlike charges. Complete separation is the zero point. As they are brought together, the two unlike charges fall into a well which is represented as a negative value. The depth of the well is how much mechanical work would be required to pull them apart again and completely separate them.