Operant Conditioning - The Law of Effect
- The law of effect basically states that responses that produce a satisfying effect in a particular situation become more likely to occur again in that situation, and responses that produce a discomforting effect become less likely to occur again in that situation.
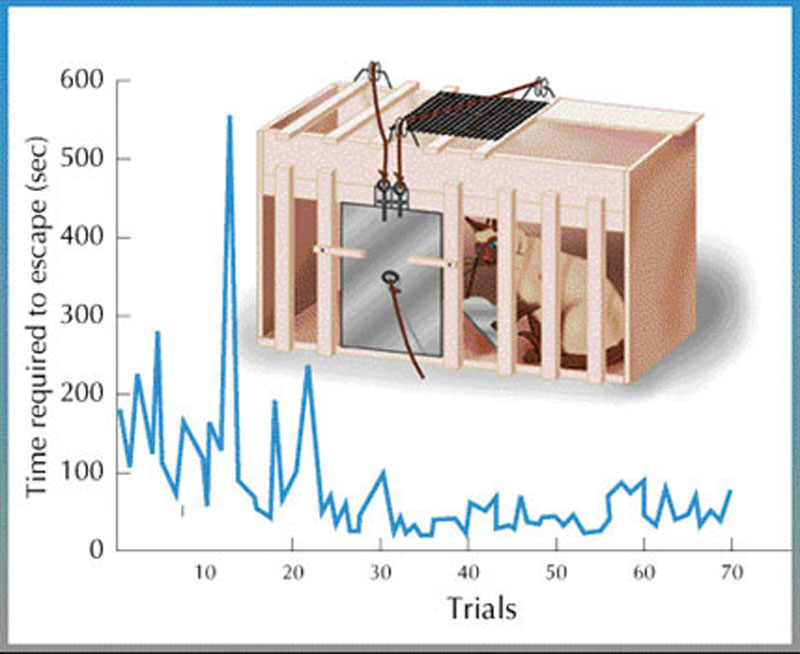
- The work of E. L. Thorndike on comparative psychology and the learning process led to the theory of connectionism and helped lay the scientific foundation for modern educational psychology.
- Thorndike meant to distinguish clearly whether or not cats escaping from puzzle boxes were using insight. Animals using a more ordinary method of trial and error in his experiments would show gradual curves. His finding was that cats consistently showed gradual learning.
- In his book The Mentality of Apes (1917) Wolfgang Köhler described observations of chimps using sticks to retrieve bananas outside of their cages. He concluded that their problem-solving method was not arrived at by trial-and-error but rather that the chimps had learned the method through insight.
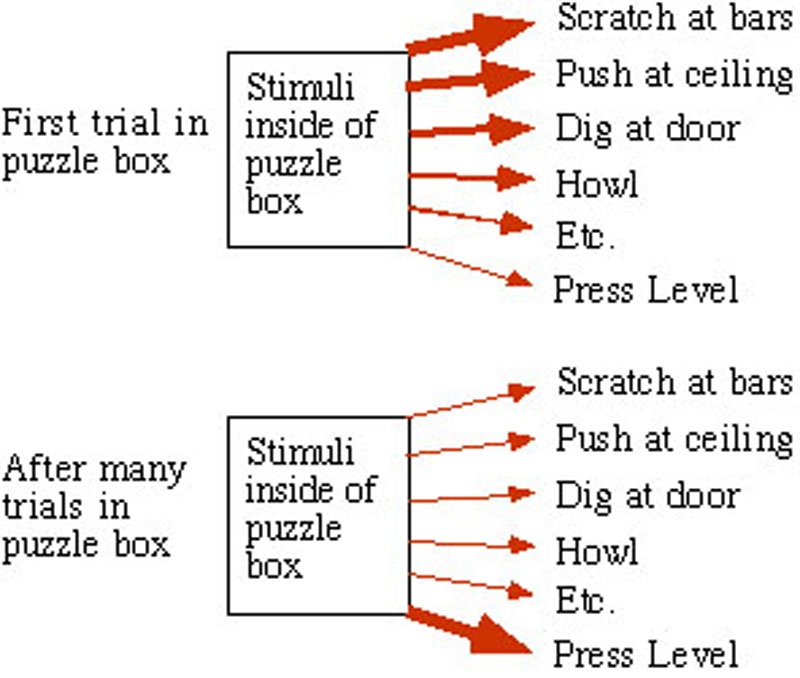
Initially, the cat’s responses were largely instinctual, but over time, the pressing lever response was strengthened while the others were weakened