Interdisciplinary Note (7 of 22)
The electronegativity difference among bonded atoms determines whether a bond is polar or nonpolar. The polarity of a molecule's chemical bonds determines the nature of the its attraction to other molecules. In addition to playing a role in determining physical properties such as boiling point, the electronegativity differences within a compound determine its solubility properties.
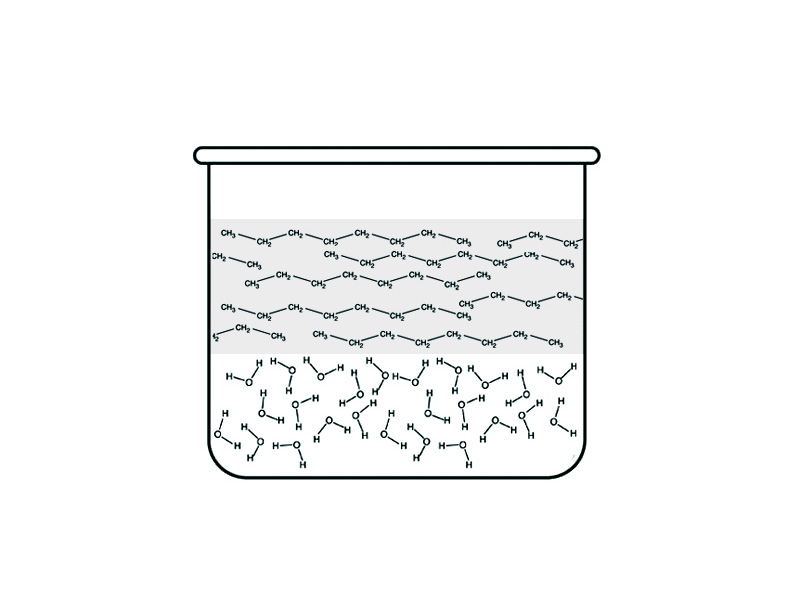
In other words, whether a molecule contains polar or nonpolar bonds determines the kinds of intermolecular force it can participate in, whether simply Van der Waals forces (also called London dispersion forces) for nonpolar molecules, dipole-dipole interaction, or hydrogen bonding.
As we discussed earlier, the nature of intermolecular force plays a crucial role in determining physical properties such as boiling point. With boiling point, we are concerned with the intermolecular attraction between a molecule and other molecules of its own type.
With solution chemistry, we are also concerned with the intermolecular attraction between the molecule and the molecules of a potential solvent. The kind of intermolecular force relationships that a substance will engage in plays a crucial role in determing the solubility properties of the substance. For the solution process, the rule is 'like dissolves like'. Polar molecules dissolve in polar solvents while nonpolar molecules dissolve in nonpolar solvents.