Interdisciplinary Note (14 of 22)
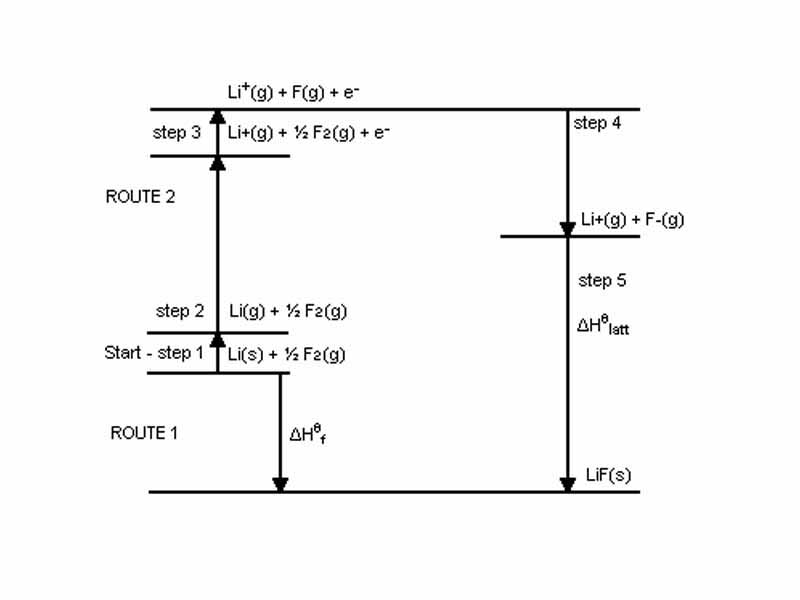
Ionic bond formation is easier to model than covalent bond formation. In Thermochemistry, we will discuss the important principle known as Hess's Law of Heat Summation, which states that the energy absorbed or evolved in any chemical reaction is fixed and independent of the path of the reaction.
Hess's Law of Heat Summation allows us to imagine a path for ionic bond formation in NaCl, for example, involving simply inputing energy to remove an electron from sodium and donating it to chlorine. The change in system energy that occurs in combining a chlorine atom and a sodium atom to form NaCl equals the sum of the ionization energy of Na and the electron affinity of Cl.