Stress
- Stress is a feeling of strain and pressure.
- A stressor is a chemical or biological agent, environmental condition, external stimulus or an event that causes stress to an organism.
- A traumatic event is an event that is severely distressing.
- In appraisal theory, primary appraisal is evaluation directed at the establishment of the significance or meaning of an event.
- In appraisal theory, secondary appraisal is evaluation directed at the assessment of the ability of the organism to cope with the consequences of the event.
- Problem-focused coping refers to one's ability to take action and to change a situation to make it more congruent with one's goals.
- Emotion-focused coping refers to one's ability to handle or adjust to the situation should the circumstances remain inconsistent with one's goals.
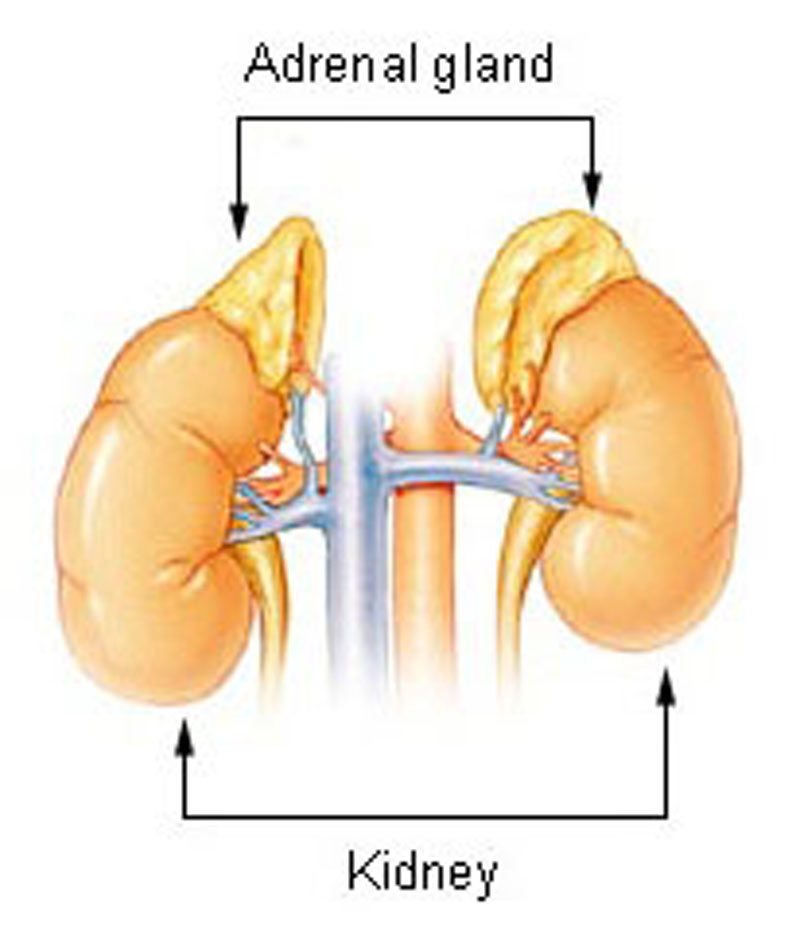
- Corticosteroids are a class of hormones produced in the adrenal cortex involved in a wide range of physiological processes including stress response, immune response, and regulation of inflammation, carbohydrate metabolism, protein catabolism, blood electrolyte levels, and behavior.
- Interactions of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and the adrenal glands constitute the HPA axis, which controls reactions to stress as well as many other processes. It is the mechanism for interactions between the endocrine system and the midbrain in the general adaptation syndrome.
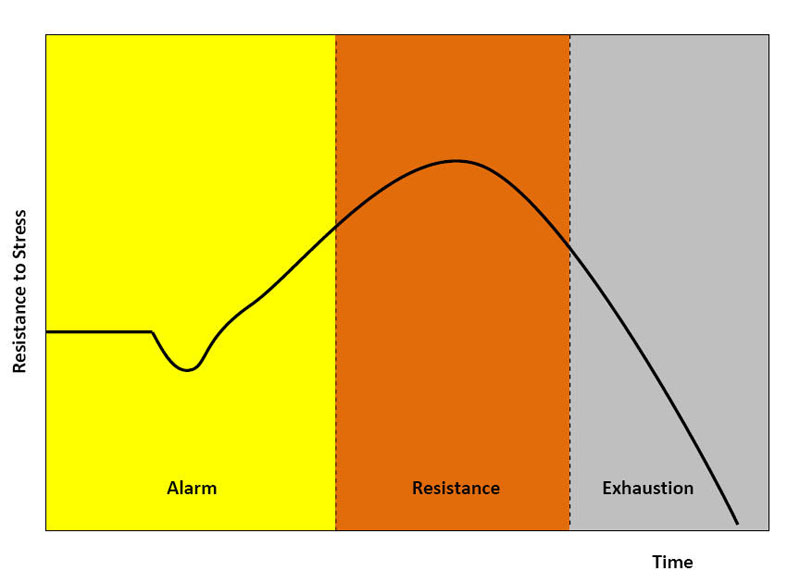
- General Adaptation Syndrome is a profile which characterizes the stress response as composed of three phases: a nonspecific mobilization phase, a resistance phase, and an exhaustion phase.
- The fight-or-flight response is a physiological reaction that occurs in response to a perceived harmful event or threat. The adrenal medulla secretes catecholamines, especially norepinephrine and epinephrine. Estrogen, testosterone and cortisol also affect how organisms react to stress.
- The tend-and-befriend response is a behavior exhibited by some animals, including humans, in response to threat. It refers to protection of offspring and seeking out the social group for mutual defense. It is theorized as having evolved as the typical female response to stress
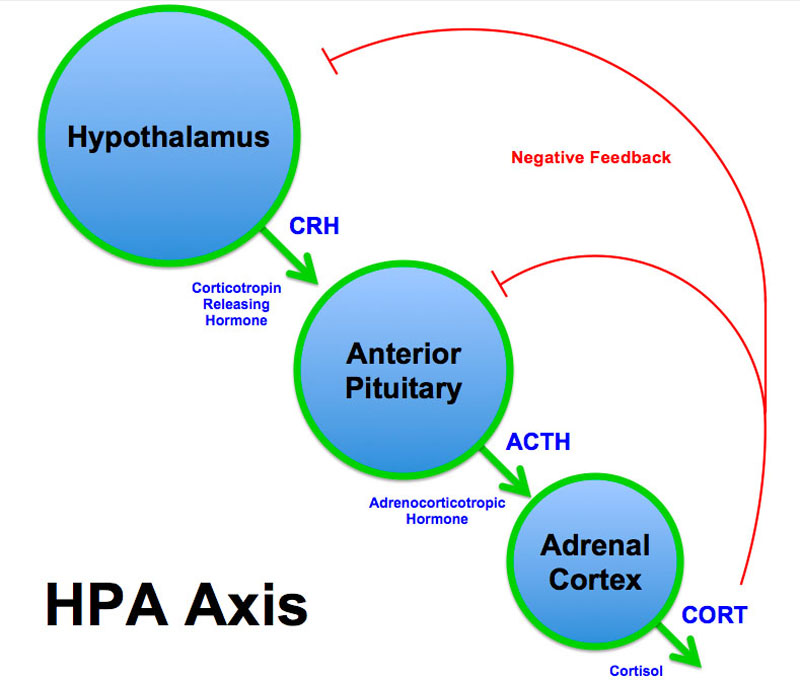
Basic hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis summary (corticotropin-releasing hormone=CRH, adrenocorticotropic hormone=ACTH).