Neurobiology of Memory
- The hippocampus belongs to the limbic system and plays important roles in the consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory and spatial navigation.
- Engrams are means by which memory traces are stored in the brain in response to external stimuli. They are sometimes thought of as neural networks and sometimes conceptualized using a hologram analogy in light of results showing that specific memories appear not to be localized.
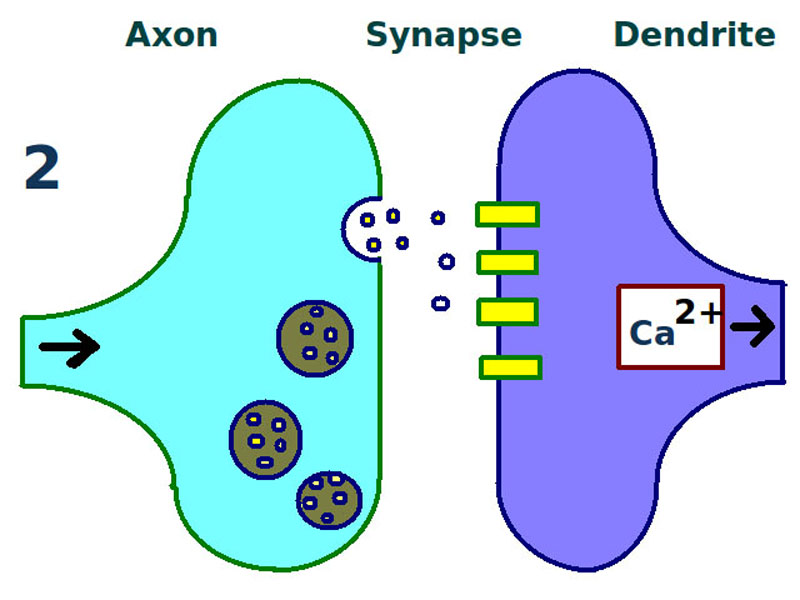
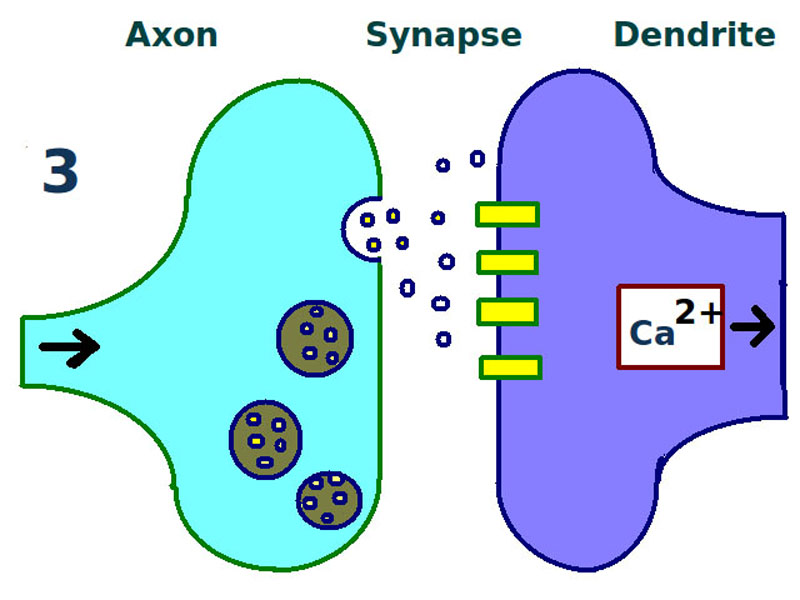
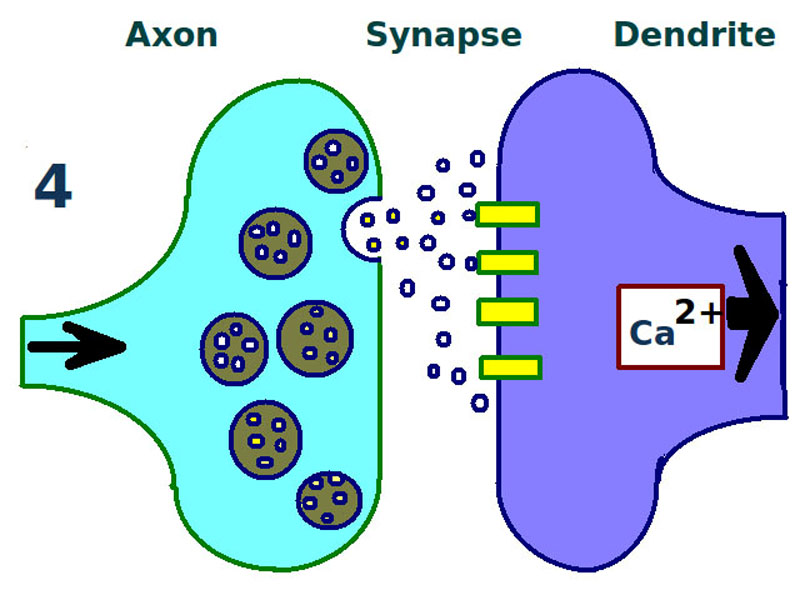
- Long-term potentiation is a persistent strengthening of synapses based on recent patterns of activity. These are patterns of synaptic activity that produce a long-lasting increase in signal transmission between two neurons.
- Memory consolidation is the category of processes that stabilize a memory trace after its initial acquisition.
- The initial process of memory consolidation, synaptic consolidation, occurs within the first few hours after learning. This involves the strengthening of synapses based on recent patterns of activity and is a form of long-term potentiation.
- Systems consolidation is the process of memory consolidation through which hippocampus-dependent memories become independent of the hippocampus over a period of weeks to years.
- A type of memory process which is amenable to detailed cellular analysis with certain animal models such as Aplysia, sensitization is a non-associative learning process in which repeated administrations of a stimulus results in the progressive amplification of a response.
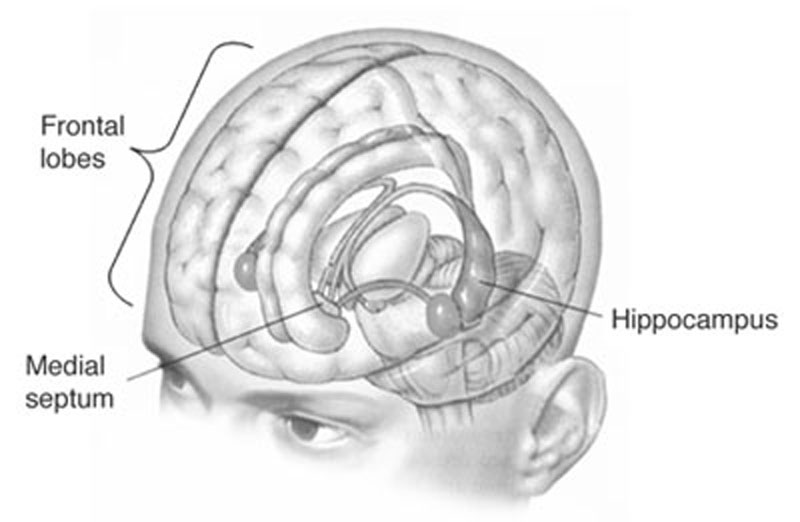
The hippocampus has long been considered the central hub of all memory, and therefore responsible for a large majority of learning. Located in the ventral-medial temporal area of the brain, its importance regarding the consolidation of new memories, and thus the learning of new things, was demonstrated by the infamous case of HM (patient), a man who had both medial temporal regions of his brain removed. This resulted in his inability to form new long-term memories.
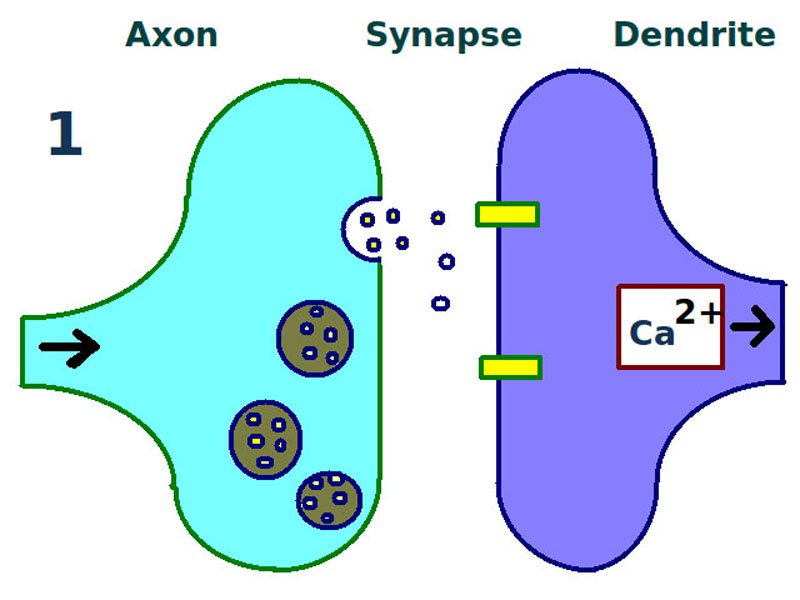
Long term potentiation: first stage. A synapse is repeatedly stimulated, sending neurotransmitters from the axon terminal (left) across the synapse to the dendrites of a second neuron (right).