Neural Tissue - Neurons
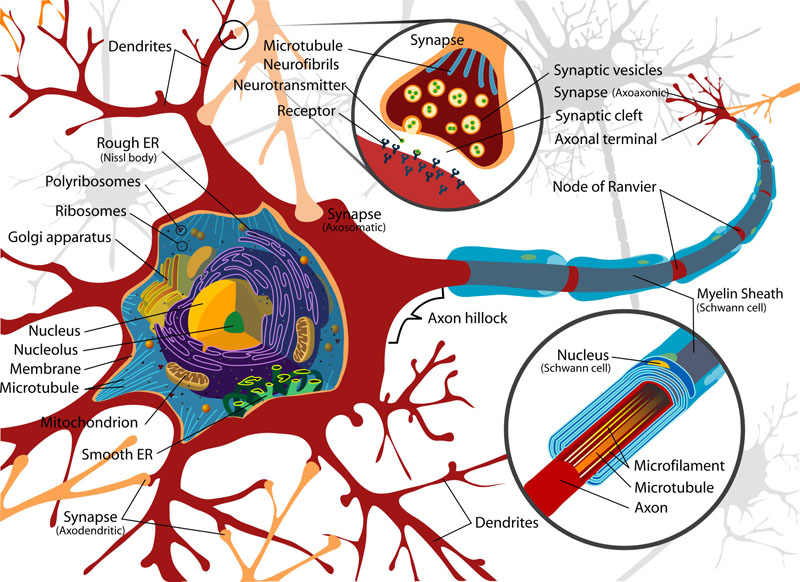
- A neuron is an electrically excitable cell that processes and transmits information through electrical and chemical signals.
- The cell body is the bulbous end of a neuron, containing the cell nucleus.
- Dendrites are the branched projections of a neuron that act to propagate the electrochemical stimulation received from other neural cells to the cell body of the neuron from which the dendrites project.
- A synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Some authors generalize this concept to include the communication from a neuron to any other cell type.
- An axon, also known as a nerve fiber, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that typically conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body.
- Axon terminals (also called synaptic boutons) are distal terminations of the branches of an axon.
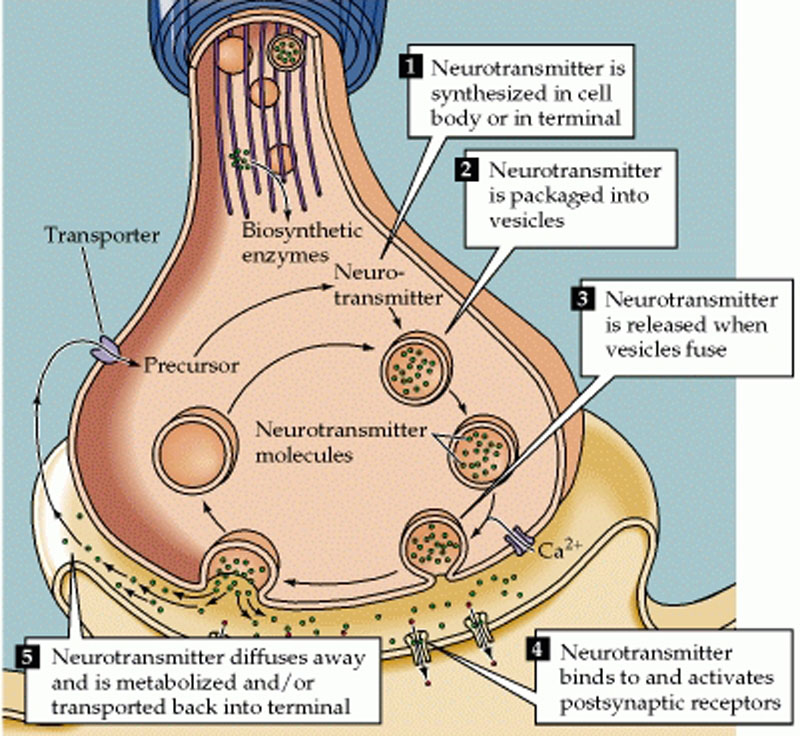
- In a neuron, synaptic vesicles store various neurotransmitters that are released at the synapse.
- Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that transmit signals across a chemical synapse, such as in a neuromuscular junction, from one neuron to another target neuron, muscle cell, or gland cell.