Mood Disorders
- Mood disorder is a group of diagnoses in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders classification system where a disturbance in the person's mood is hypothesized to be the main underlying feature.
- Major depressive disorder is a mental disorder characterized by a pervasive and persistent low mood that is accompanied by low self-esteem and by a loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities.
- A major depressive episode is a period characterized by the symptoms of major depressive disorder.
- Anhedonia is defined as the inability to experience pleasure from activities usually found enjoyable, e.g. exercise, hobbies, music, sexual activities or social interactions.
- Dysthymia is a mood disorder consisting of the same cognitive and physical problems as in depression, with less severe but longer-lasting symptoms.
- Behavioral activation is an idiographic and functional approach to depression. It argues that people with depression act in ways that maintain their depression and locates the origin of depressive episodes in the environment.
- The monoamine hypothesis of depression, postulates that the deficit of certain neurotransmitters is responsible for the features of depression.
- Monoamines are neurotransmitters and neuromodulators that include serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine.
- Beck's cognitive triad represents three types of negative thoughts present in depression. These are thoughts about the self, the world, and the future.
- A negative schema is a fundamental underlying way in a which a person processes information reflecting a negative view of the self, the world, or the future.
- Cognitive distortions are exaggerated or irrational thought patterns that are believed to perpetuate the effects of psychopathological states, especially depression and anxiety.
- Seasonal affective disorder is a mood disorder subset in which people who have normal mental health throughout most of the year experience depressive symptoms in the winter or summer.
- Bipolar disorder is a mental disorder characterized by periods of elevated mood and periods of depression. The elevated mood is significant and is known as mania or hypomania depending on the severity or whether there is psychosis.
- Bipolar I disorder is a bipolar spectrum disorder characterized by the occurrence of at least one manic or mixed episode.
- Bipolar II disorder is a bipolar spectrum disorder characterized by at least one episode of hypomania and at least one episode of major depression. Diagnosis requires that the individual must never have experienced a full manic episode.
- Mania is the mood of an abnormally elevated arousal energy level, or "a state of heightened overall activation with enhanced affective expression together with lability of affect.
- Hypomania is a mood state characterized by persistent disinhibition and pervasive elevated (euphoric) or irritable mood but generally less severe than full mania.
- Cyclothymia is a type of chronic mood disorder widely considered to be a more chronic but milder or subthreshold form of bipolar disorder.
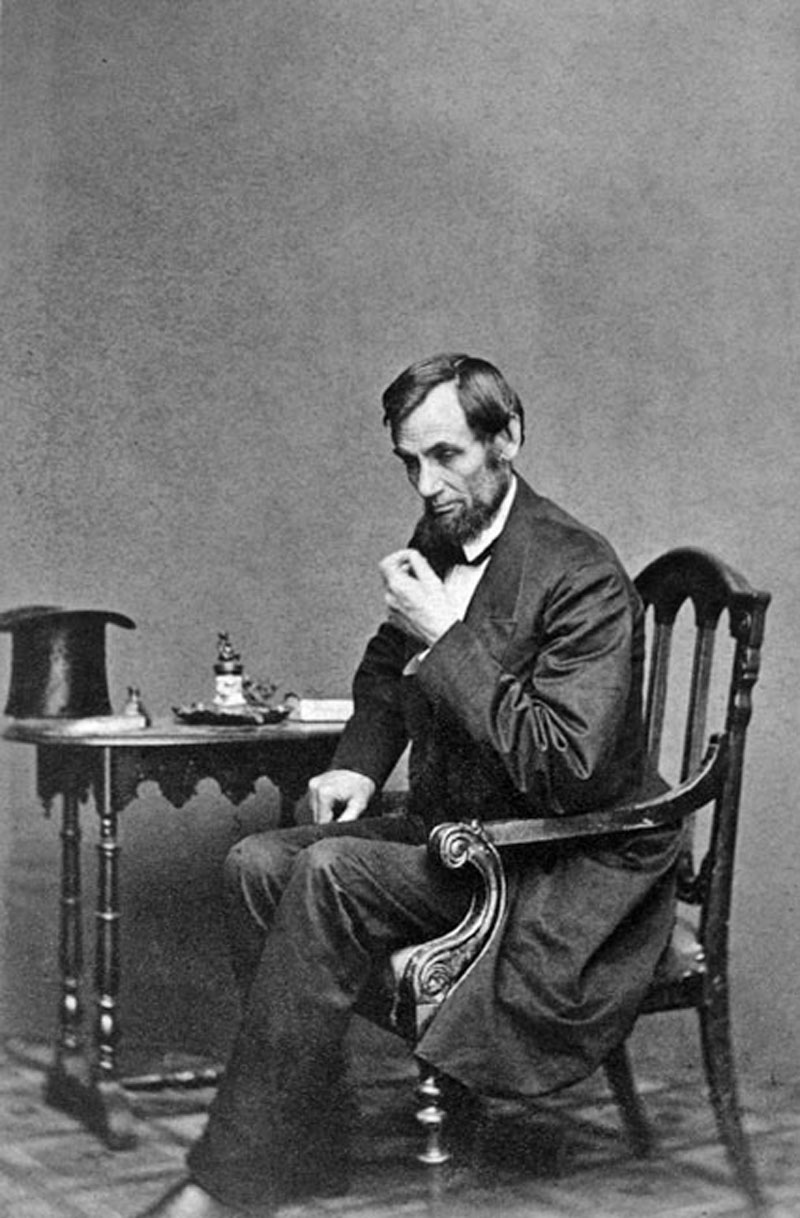

Abraham Lincoln suffered from 'melancholy', a condition that now may be referred to as clinical depression.
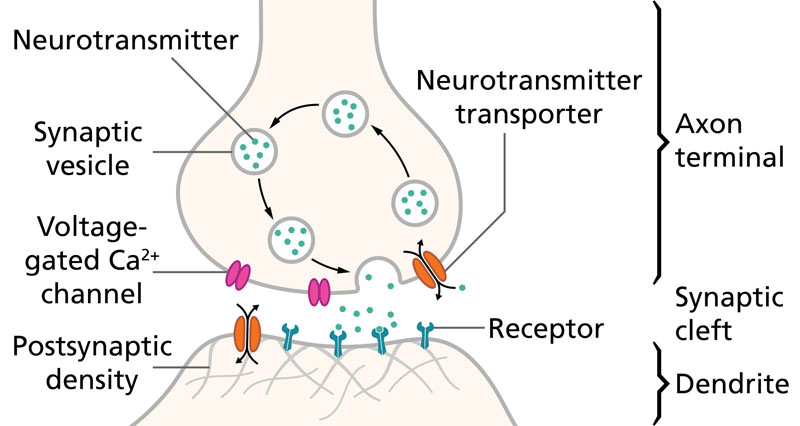
Diagram of a chemical synapse between two neurons. Most antidepressants influence the overall balance of three neurotransmitters: serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. Some antidepressants act on neurotransmitter receptors.
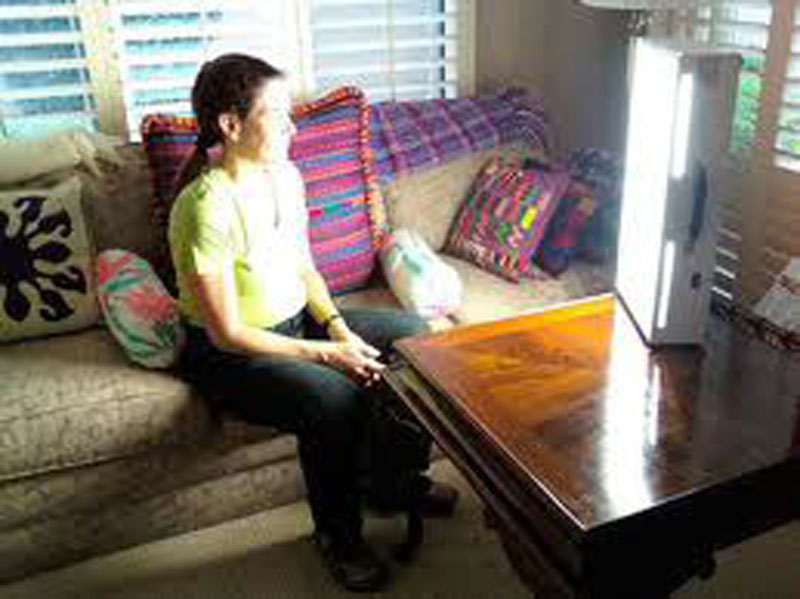

Bright light therapy is a common treatment for seasonal affective disorder and for circadian rhythm sleep disorders.