Impulse Transmission within Nerve Fibers
- The relatively static membrane potential of quiescent cells is called the resting membrane potential, as opposed to the specific dynamic electrochemical phenomena called action potential and graded membrane potential.
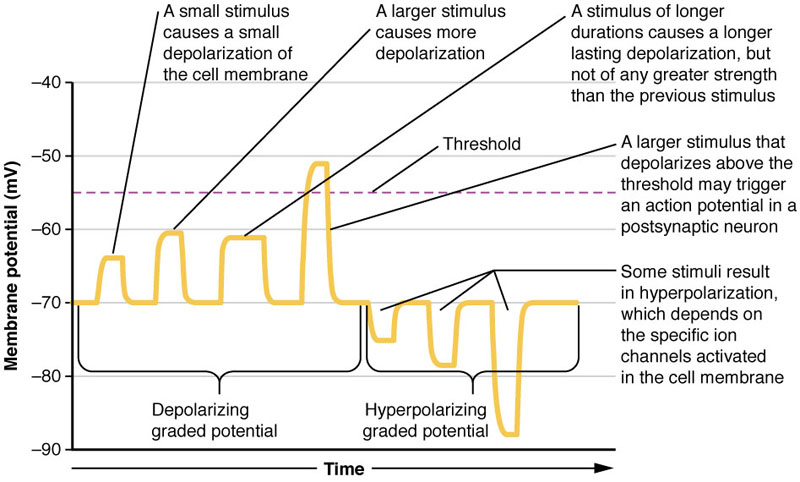
- Graded potentials are changes in membrane potential that vary in size, as opposed to being all-or-none.
- The threshold potential is the critical level to which the membrane potential must be depolarized in order to initiate an action potential.
- An action potential is a short-lasting event in which the electrical membrane potential of a cell rapidly rises and falls, following a consistent trajectory.
- The refractory period is the amount of time it takes for an excitable membrane to be ready for a second stimulus once it returns to its resting state following an excitation.