Interdisciplinary Note (11 of 36)
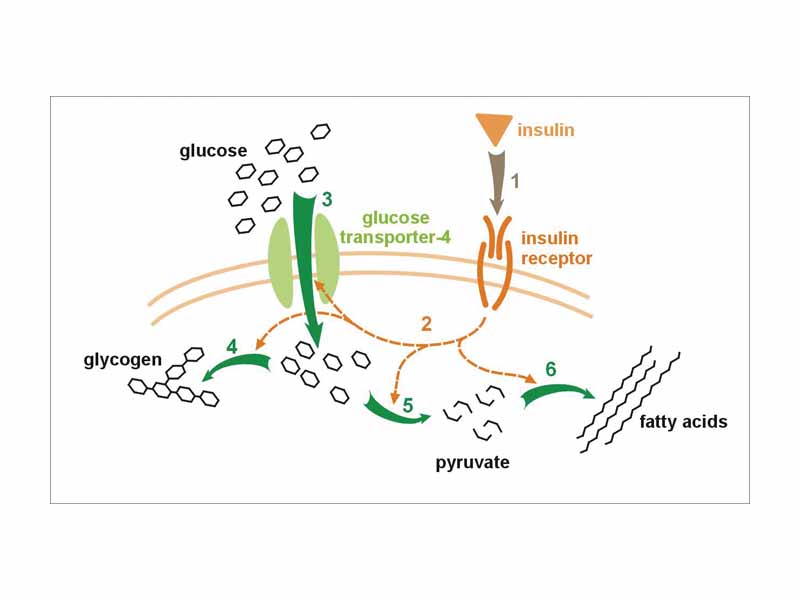
Effect of insulin on glucose uptake and metabolism. Insulin binds to its receptor (1) which in turn starts many protein activation cascades (2). These include: translocation of Glut-4 transporter to the plasma membrane and influx of glucose (3), glycogen synthesis (4), glycolysis (5) and fatty acid synthesis (6).
In response to chemoreceptors monitoring blood glucose levels in the hypothalamus, parasympathetic neurons extending from the hypothalamus stimulate beta cells (producing insulin and lowering blood glucose) if blood glucose is too high; sympathetic neurons stimulate alpha cells if blood glucose is too low, as well as causing beta cells to reduce insulin secretion.